FDA IND Approval of AI-derived Cancer Drug ISM3091 Marks a Milestone for Insilico Medicine
In an essential leap forward for the utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) in drug discovery, Insilico Medicine secured Investigational New Drug (IND) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its AI-generated USP1 inhibitor, ISM3091. This nod of approval greenlights Insilico to proceed with clinical trials of this promising oncology therapeutic in both the U.S. and China.
Dr. Sujata Rao, Senior Vice President and Head of Global Clinical Development at Insilico, applauded the FDA's recognition of ISM3091's potential and the consequent initiation of human trials at various clinical locations.

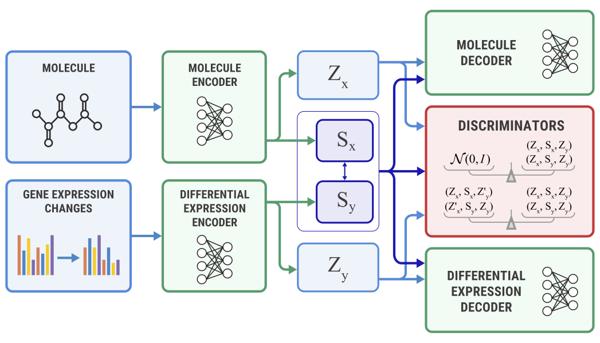
The company capitalized on its proprietary AI platform, Chemistry42, to successfully identify and design ISM3091 alongside another promising drug candidate, ISM001-055. Currently in clinical trials for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), ISM001-055 is poised as a potential first-in-class small molecule inhibitor. These developments underline the transformative potential of AI in expediting drug discovery processes while cutting down associated expenses.
Ubiquitin-specific protease 1 (USP1) inhibitors like ISM3091 have been the subject of attention in oncology due to their potential to augment the efficacy of anti-cancer therapeutics. USP1, an enzyme with roles in DNA damage repair, is seen in higher levels in several types of cancers. Inhibitors of USP1 could potentially enhance cancer therapy outcomes by reducing survivin levels and increasing DR5 through miR-216a-5p.
In the battle against resistance to PARP inhibitors, a well-known stumbling block in cancer therapy, ISM3091 shows substantial promise. Preclinical investigations demonstrated the potency of ISM3091 against a variety of tumour cell lines, particularly those with BRCA1 mutations. Furthermore, Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) toxicology assessments have revealed minimal gastrointestinal or hematological toxicity and favourable overall pharmacokinetics.
In its IND application to the FDA, Insilico provided an intricate clinical trial design, from patient selection strategies to safety monitoring protocols. Dr. Rao emphasized the significance of preserving the quality and safety of ISM3091 as it transitions into Phase 1 human trials.
The IND clearance stands to bring strategic benefits to Insilico in the form of potential partnerships, financial backing, and increased stakeholder engagement. Dr. Rao spotlighted the transformational ability of AI in streamlining drug development, minimizing associated risks, costs, and protracted timelines inherent in traditional methods.
The upcoming multicenter Phase 1 trial of ISM3091 aims to assess the drug's safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and early indications of efficacy in patients with advanced solid tumours. The trial will be open to patients with BRCA-mutated breast, ovarian, and HRD (including BRCA-mutated) prostate cancers.
As Insilico continues to make strides in the realm of drug discovery, it strengthens its standing as a pioneer in AI-aided medicine. The advancements with ISM3091 and the ongoing progress of ISM001-055 underscore the effectiveness of its AI-fueled platform in accelerating drug discovery. Looking ahead, ISM3091 is slated for evaluation in a wider range of patient populations, potentially in tandem with PARP inhibitors and other investigational agents.
Topics: AI & Digital