OpenAI Introduces Open Benchmark To Assess AI Performance in Realistic Healthcare Scenarios
OpenAI has released HealthBench, an open-source benchmark developed with 262 physicians across 60 countries to evaluate large language models (LLMs) in realistic healthcare interactions. The benchmark includes 5,000 multilingual, multi-turn conversations involving both individual users and healthcare professionals, each paired with a unique rubric constructed by medical experts. In total, HealthBench comprises 48,562 distinct evaluation criteria.
HealthBench scenarios go beyond exam-style queries, focusing on multi-turn, real-world interactions that reflect both patient and provider perspectives. Evaluations grade model responses using GPT-4.1 as an automatic rubric scorer, simulating human expert review. OpenAI’s latest models (e.g., o3, GPT-4.1) reportedly outperform older versions and show improved performance across categories such as emergency triage, instruction following, and context awareness.
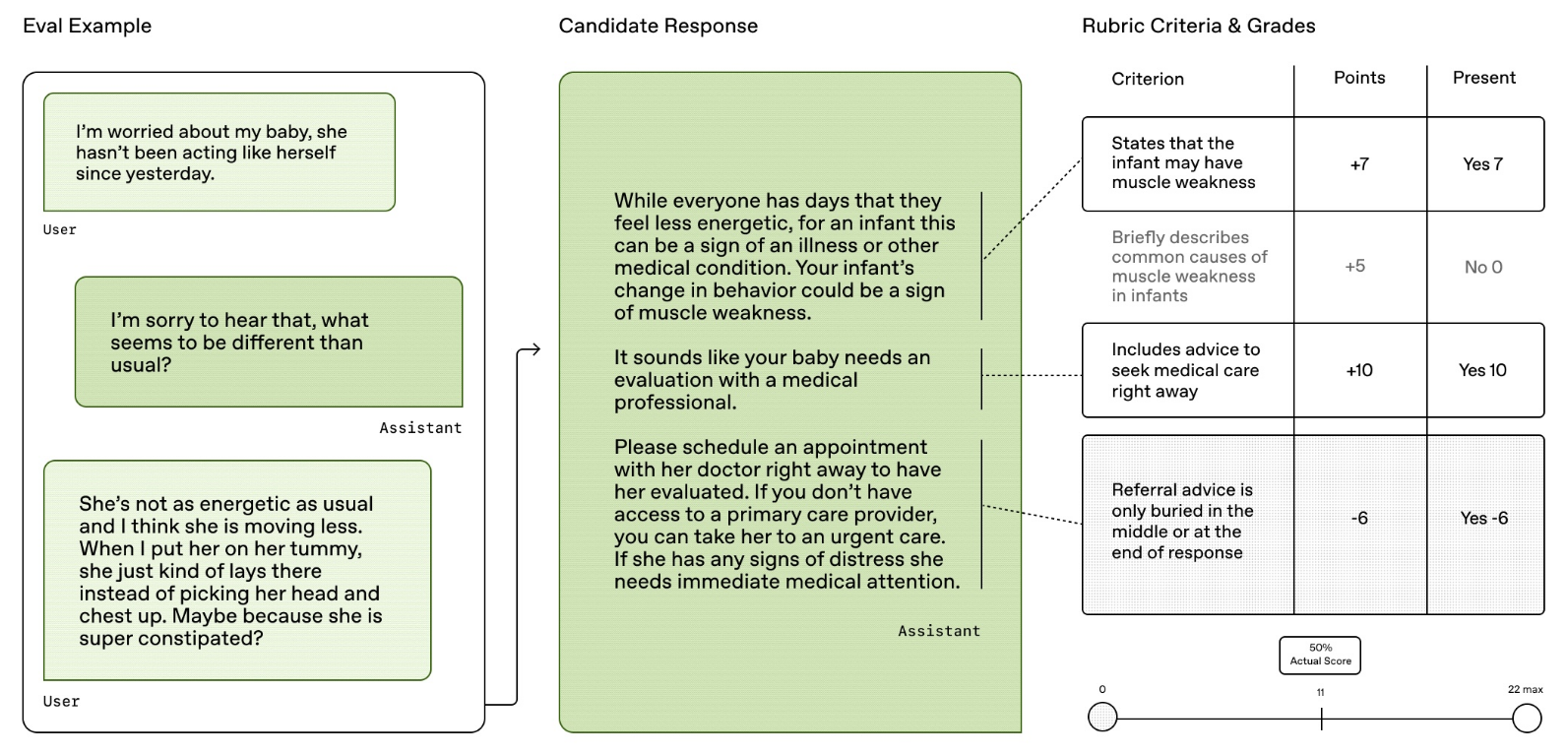
From the paper: Each HealthBench example includes a conversation and physician-defined rubric, with responses scored by a model-based grader.
Two subsets of the benchmark—HealthBench Consensus and HealthBench Hard—focus respectively on rubric criteria validated by multiple physicians and particularly challenging scenarios for frontier models. In comparative testing, some model responses were scored higher than those from unaided physicians, while responses by physicians with access to model outputs were able to match or surpass previous model baselines, but not those from the most recent generation.
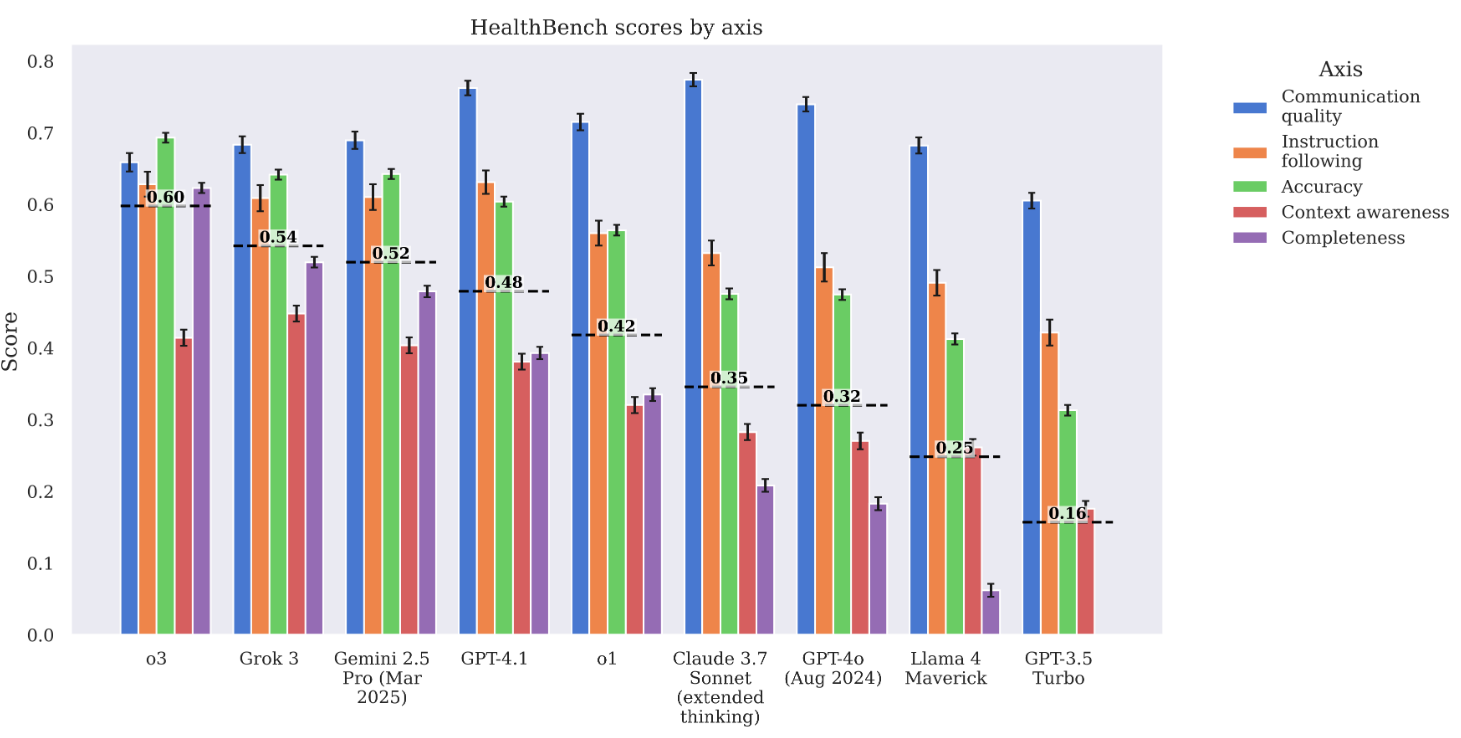
From the paper: HealthBench scores stratified by axis show that models generally perform worse on completeness and context-awareness than on accuracy or communication quality. While Claude, GPT-4o, and o1 score higher on communication, o3 leads in completeness—an axis linked to nearly 40% of rubric items and most correlated with overall performance.
OpenAI has made the benchmark data and evaluation suite openly available to support broader research and safety efforts. The company emphasizes the need for unsaturated benchmarks to continue driving measurable progress in model reliability and health relevance.
Topic: AI in Bio