Deep Genomics Releases AI Foundation Model for microRNA Binding and mRNA Degradation Prediction
Deep Genomics has introduced REPRESS, a deep learning model trained to predict microRNA (miRNA) binding and mRNA degradation directly from nucleotide sequence—two core mechanisms that determine mRNA stability and influence protein levels. The model is described as the first foundation model to address these post-transcriptional events from sequence alone, and is now integrated into Deep Genomics’ multi-model Foundation Model Platform.
REPRESS was trained on millions of experimentally validated sites from human and mouse tissues. According to the company, it outperforms seven existing methods across multiple benchmarks, including variant effect prediction and both canonical and non-canonical repression modeling. It is designed to support antisense oligonucleotide (ASO), siRNA, and mRNA therapeutic programs by enabling more precise target selection and modulation of gene expression.
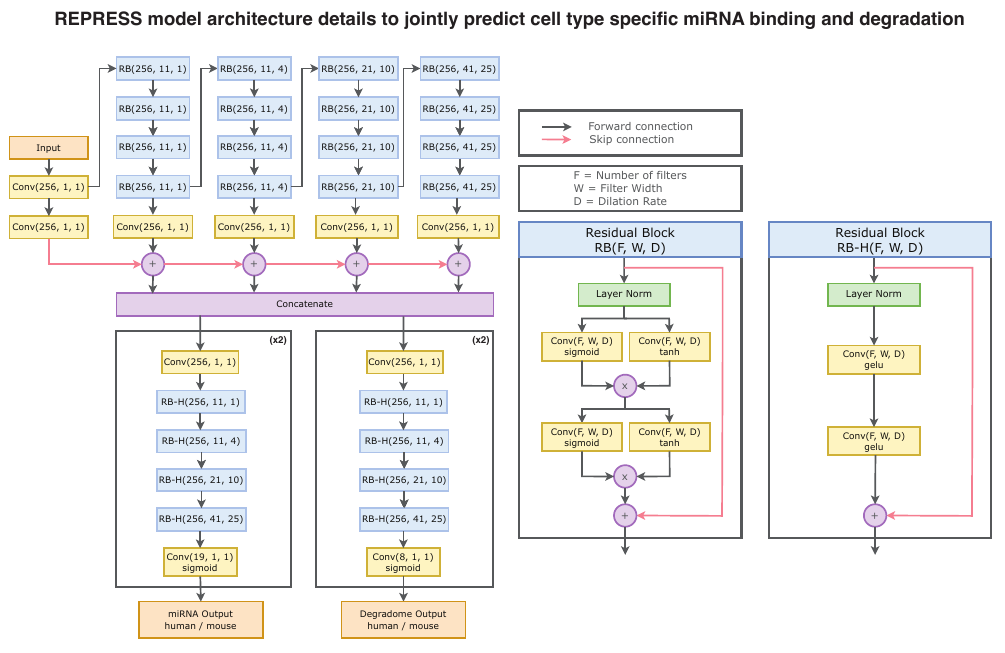
The model complements Deep Genomics’ prior work on RNA splicing and editing, forming what the company describes as a cohesive, interoperable AI platform for end-to-end genomic R&D.
The REPRESS model is now available for non-commercial academic use via GitHub, allowing external researchers to explore mRNA stability mechanisms in disease and drug development contexts.
bioRxiv source: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.05.15.654105v1
Topic: AI in Bio