Insilico Medicine Presents Eight Oral Cardiometabolic Drug Candidates Designed With AI
On November 7, 2025 at BIO-Europe, Insilico Medicine disclosed eight oral small-molecule programs for cardiometabolic diseases discovered with its Pharma.AI platform. The portfolio spans lead identification to IND-enabling and targets GLP-1R, GIPR, dual amylin/calcitonin receptors (DACRA), APJ, Lp(a), NLRP3, and NR3C1. The set is designed for low-dose combinations and includes a fully biased oral GLP-1R agonist intended for once-weekly dosing.
Insilico frames its approach as multi-parameter-optimized generative design aimed at oral bioavailability, longer half-life, and safety suitable for combinations. The company highlights a brain-penetrant NLRP3 inhibitor (ISM8969) at IND-enabling and a selective NR3C1 antagonist nearing PCC for hypercortisolism-linked disease.
The unveiling of Insilico Medicine’s cardiometabolic portfolio comes at a time when GLP-1 receptor agonists are being increasingly discussed not just as metabolic drugs, but as possible first-in-class longevity therapeutics. At the 12th Aging Research and Drug Discovery Meeting (ARDD2025) in Copenhagen, Eli Lilly’s Andrew Adams made the case that GLP-1s—traditionally used for diabetes and obesity—may be the most scalable clinical tool yet for delaying age-related diseases and compressing morbidity. Novo Nordisk’s Lotte Bjerre Knudsen went even further, titling her talk "Semaglutide as a Proven Longevity Medicine."
Insilico founder and CEO Alex Zhavoronkov sees the company’s newly announced GLP-1RAs as part of "the first wave of longevity therapeutics," citing their potential to impact both healthspan and lifespan. Insilico’s strategy, he explains, was to combine established and moderate-novelty targets with novel chemistry and multi-parameter design focused on properties that would enable safe, low-dose combinations across cardiometabolic and age-linked pathways. Among the most advanced candidates are oral, fully biased GLP-1R agonists with "a very high level of preclinical safety tested in multiple species," including one molecule engineered for sustained, once-weekly dosing—an attribute that could be critical for long-term adherence in aging populations.
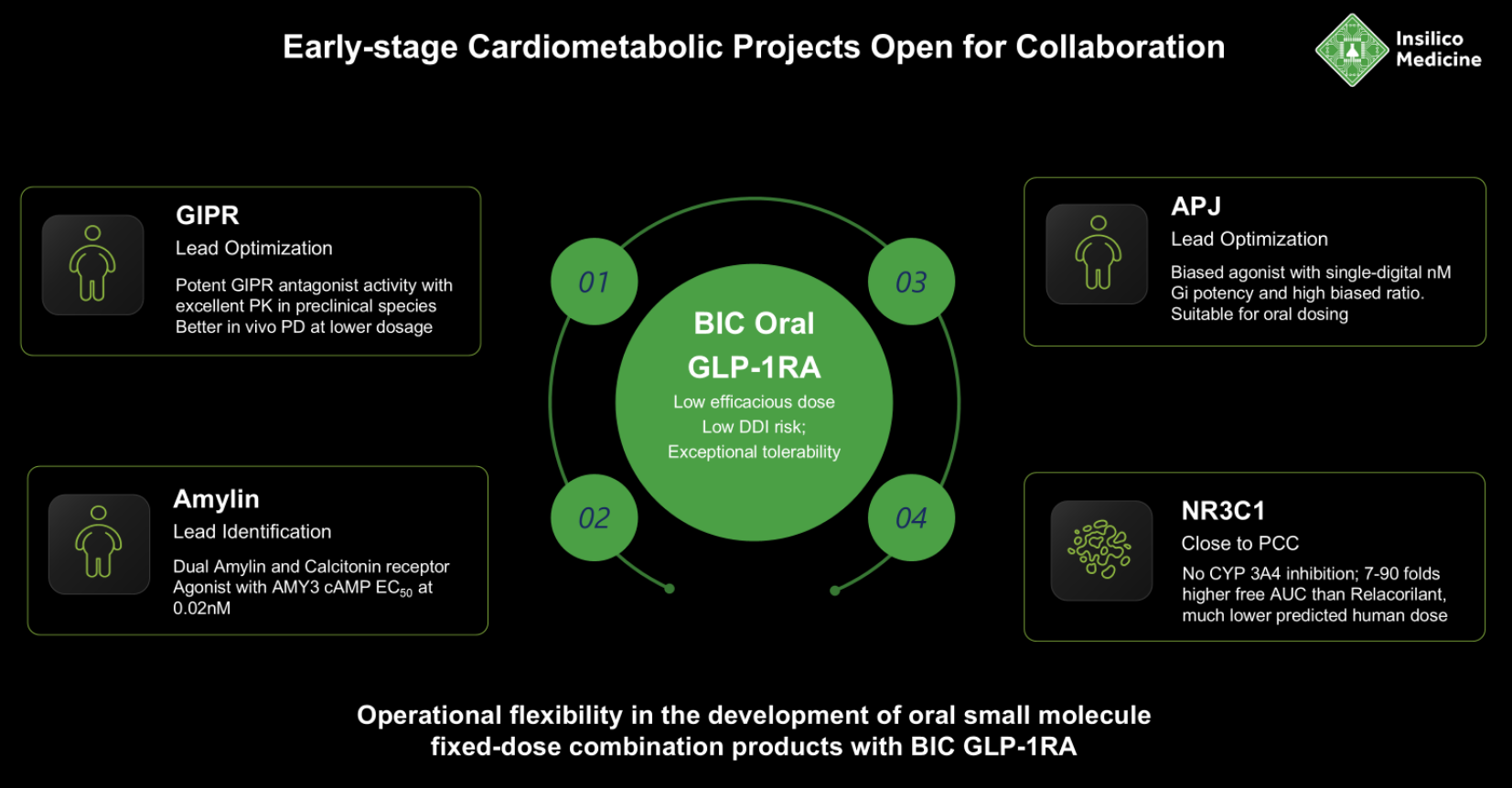
Source: Insilico Medicine
AI-Generated Cardiometabolic Assets
-
GLP-1RA (QD) — IND-enabling. Fully biased once-daily oral GLP-1R agonist with low microsomal clearance, minimal CYP inhibition, and favorable cross-species PK; reportedly delivers long-term anti-obesity effects alongside acute food-intake and glucose-control effects.
-
GLP-1R (QW) — Pre-development candidate. Fully biased oral GLP-1R agonist engineered for once-weekly dosing; high solubility, extremely low metabolic/systemic clearance, and long predicted half-life; weight-loss efficacy reportedly comparable or superior to daily oral GLP-1RAs.
-
NR3C1 — Close to PCC. Selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist with strong solubility/permeability and no CYP3A4 inhibition; higher exposure and improved in-vivo efficacy vs other NR3C1 inhibitors; reportedly reverses cortisol-induced metabolic dysfunction and enhances semaglutide-mediated weight loss; positioning includes orphan-eligible Cushing’s and broader hypercortisolism-linked disease.
-
NLRP3 (ISM8969) — IND-enabling. Orally available, brain-penetrant, selective NLRP3 inhibitor with favorable in-vitro safety/PK; robust efficacy in models of Parkinson’s disease, peritonitis, pancreatitis, and multiple sclerosis; described by Insilico as potentially best-in-class vs peripherally restricted competitors.
-
Dual Amylin & Calcitonin Receptor Agonist (DACRA) — Lead identification. Potent dual agonist with novel structure and high receptor potency, designed to enhance satiety, reduce food intake, and improve glycemic control.
-
GIPR (antagonist) — Lead optimization. Next-generation GIPR antagonist intended to complement GLP-1-based regimens; high predicted receptor selectivity, optimized metabolic stability, and favorable oral bioavailability; advanced for synergistic efficacy and improved tolerability in combinations.
-
APJ (biased agonist) — Lead optimization. Potent, highly G-protein-biased APJ agonist with novel scaffold; bias is intended to avoid β-arrestin effects associated with hypertrophy/inflammation; in DIO (diet-induced obesity) mice, oral dosing lowered blood glucose, reduced body weight, and improved lean-mass ratio.
-
Lp(a) — Lead optimization. Novel-structure small molecule with higher AUC and longer half-life in animals; in transgenic mouse models, Lp(a) lowering comparable to a clinically validated candidate; less off-target plasminogen inhibition after 5-day BID dosing.
Insilico’s new cardiometabolic portfolio extends a broader effort to industrialize drug discovery through generative AI. The company has advanced 22 preclinical candidates within 12–18 months each—roughly half the conventional timeline—and now counts several clinical-stage programs in fibrosis, oncology, and inflammation. Its anti-fibrotic candidate Rentosertib recently completed a Phase 2a trial with results published in Nature Medicine, while ISM5411, a gut-restricted PHD1/2 inhibitor for inflammatory bowel disease, has cleared Phase I. With six papers in the Nature portfolio since 2024, Insilico continues to present itself as a case study in how AI-driven design can accelerate therapeutic development across diverse disease areas.
Topic: AI in Bio