Artificial Intelligence For Drug Discovery Use Cases At Mind the Byte
UPDATE: Mind the Byte ceased operations and was liquidated in 2019.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a hot topic in the biopharmaceutical environment and nearly every pharma company in the world has embraced it hoping that it will play a major role in speeding up drug discovery, by reducing R&D costs and avoiding failure in late development stages. According to prospects, AI-driven drug discovery will lead to the development of new and more effective drugs, paving thus the way to personalized medicine.
Machine learning (ML) techniques, a particular approach to artificial intelligence, are currently being used at Mind The Byte to develop new In Silico tools for Drug Discovery as well as for the improvement of classical CADD techniques. Different supervised learning algorithms; artificial Neural Networks (aNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM) and Random Forest (RF), are being applied in four different research areas: ADMET modeling, In Silico MedChem, QSAR and Docking:
(To know more about other AI use cases in drug discovery read our recent review "How Pharmaceutical And Biotech Companies Go About Applying Artificial Intelligence in R&D")
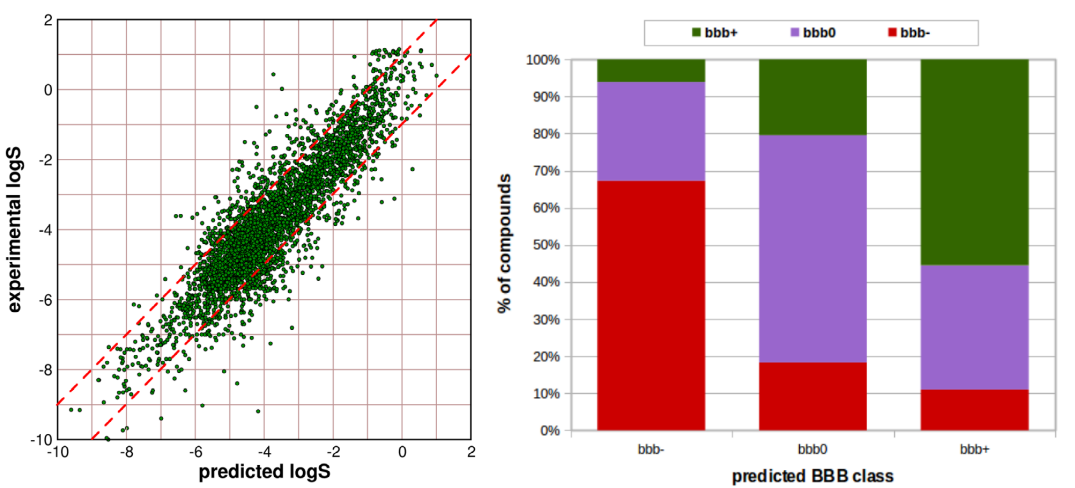
ADMET modeling: In order to support selection of druggable chemotypes among screening hits and potential target molecules, we have developed a set of relevant predictive in silico models. Using in vitro data extracted from different databases and publications, conveniently mined, curated and standardized, different ADME predictive models have been generated using the different ML modeling techniques previously summarized. Developed ADME models include physicochemical (logP, logS) and pharmacokinetic (Caco-2, BBB, %PPB, Pgp and hERG) properties.
In Silico MedChem: Several approaches can be envisaged to transform a hit originating from a public domain source to patentable chemotypes. At Mind the Byte, we have developed an algorithm for hit optimization based on the molecular fragmentation of the query molecule which considers synthetic concepts right from the very beginning. The combination of different molecular reconstruction schemas and the collection of identified isosteric fragments might yield a chemical space eventually containing hundreds of millions of virtual compounds. Navigation and exploration of such large spaces cannot be accomplished unless AI techniques are applied. In this case, genetic algorithms (GAs) are the ultimately responsible for identifying the optimal compound collection fulfilling the requirements of a given multiobjective fitness function.
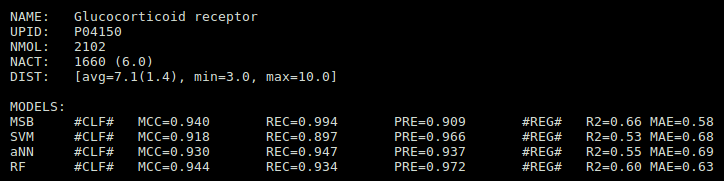
QSAR: Quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling is one of the most useful computer-aided tools employed in drug discovery, especially in the absence of 3D structures for specific drug targets. As it is common knowledge that several drugs interact with many biological targets and that this polypharmacology has a direct implication in both therapeutic efficacy and safety, more efficient and fully automated multi-target approaches are required. In this context, multi-target QSARs will permit to predict the full activity profile of a given compound against a panel of different biological targets, leading to the development of target profiling and target fishing applications.
Therefore, we have developed SmartQSAR, an intelligent system that combines machine learning (aNN, SVM and RF) and molecular similarity-based (MSB) calculations to predict ligand-target activities directly from 2D molecular representations. SmartQSAR includes binary classifiers (CLF) and regression models (REG) that have been trained using ligand-target quantitative activity data on a panel of ca. 3000 drug targets.
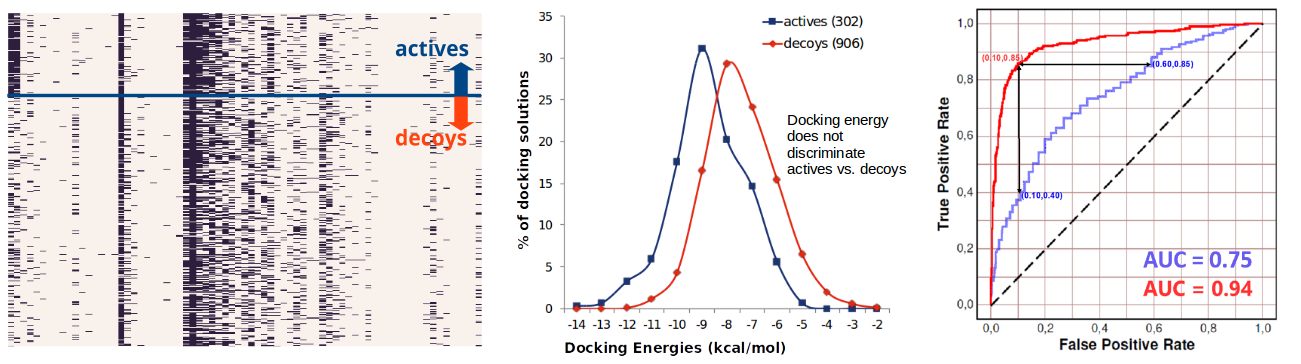
Docking: Computational docking is widely used in drug discovery for the study of protein-ligand interactions and as a tool for virtual screening and virtual profiling. However, despite recent improvements in docking and scoring methods, docking calculations are still challenged by the identification of enormous amounts of false positives.
To address this issue, focus must necessarily be redirected towards the process of binding itself, a dynamic process, the temporal stability of which is often linked to the ability of the ligand to form specific molecular interactions with the target protein. Thus, making use of the enormous amount of structural data deposited on the PDB, we have developed an “intelligent” system (SmartDock) aimed at the reduction of false positives in docking experiments by elucidating the pattern of specific protein-ligand interactions extracted from the experimental binding information in PDB.
This computational engine was initially validated with excellent results on PARP1, a protein involved in DNA damage repair having an important role in both cancer and aging. In this case example, SmartDock outperformed traditional enrichment processes, providing an AUC value of 0.94 in contrast to the 0.75 obtained when a simple docking energy cutoff was applied. The advantage can also be illustrated with the middle graph showing only a modest separation between active PAPR1 ligands and decoy compounds using energy-based scoring.
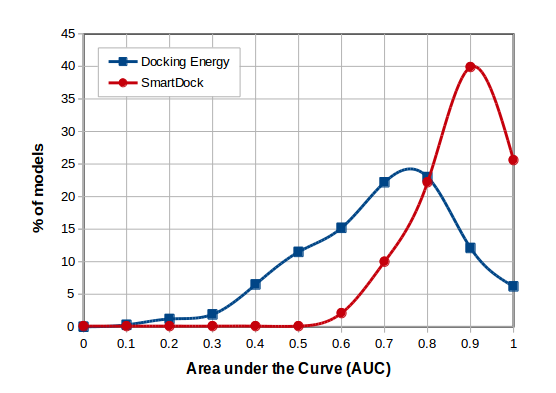
SmartDock is currently being extensively exploited on a set of circa 700 drug targets and its good overall performance (Figure below) in comparison with docking energy, represents an important milestone for the promotion of ligand docking methods to the next level, i.e. their use as reliable in silico screening/profiling tools in drug discovery.
Future perspectives
At Mind the Byte, we have already started to plan our future development priorities. Among them, our top priority is the integration of machine learning techniques and systems pharmacology as a requirement for the development of specific in silico pharmacology tools with potential impact in different areas of drug discovery, especially in the identification of new therapeutic strategies and novel therapeutic uses of already approved drugs, the discovery of new potential disease therapies for complex diseases and, more interestingly, for the development of personalized medicine applications.
Topic: AI in Bio