NVIDIA Releases Agentic AI Blueprint for Literature Review and Target Discovery
NVIDIA has released a new AI-driven workflow, the Biomedical AI-Q Research Agent Developer Blueprint, designed to accelerate the early phases of drug discovery by automating literature review and hypothesis generation. Built on top of NVIDIA’s AI-Q and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) blueprints, the system combines a reasoning agent with virtual screening capabilities, targeting use cases such as target identification and small molecule pairing.
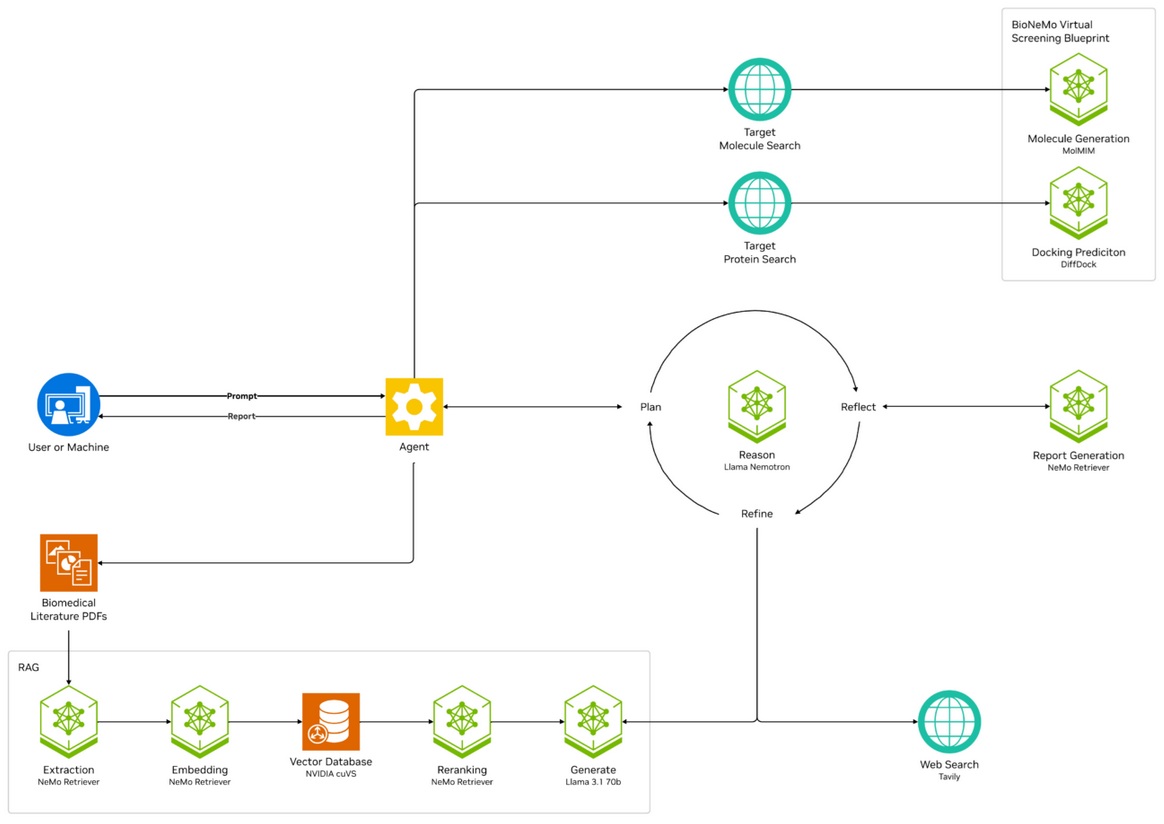
A system diagram of technical components; NVIDIA
The system uses Meta’s Llama-based Nemotron model to ingest and synthesize data from more than 100 scientific papers in minutes, a process that typically takes researchers several hours per paper. According to NVIDIA, this reasoning agent can propose complex hypotheses (e.g. evaluating factors like molecular binding affinity, synthesis feasibility, and potential clinical viability) before passing outputs to the BioNeMo virtual screening module for downstream analysis of protein–ligand interactions.
See also: The Rise of AI Agents in Biotech, Where Are We Now?
This creates a multi-agent, modular pipeline capable of simulating portions of the preclinical ideation process. NVIDIA claims that it can help address one of the most time-intensive stages of drug discovery—literature mining and early hypothesis formation—which historically consumes up to 30% of timelines.
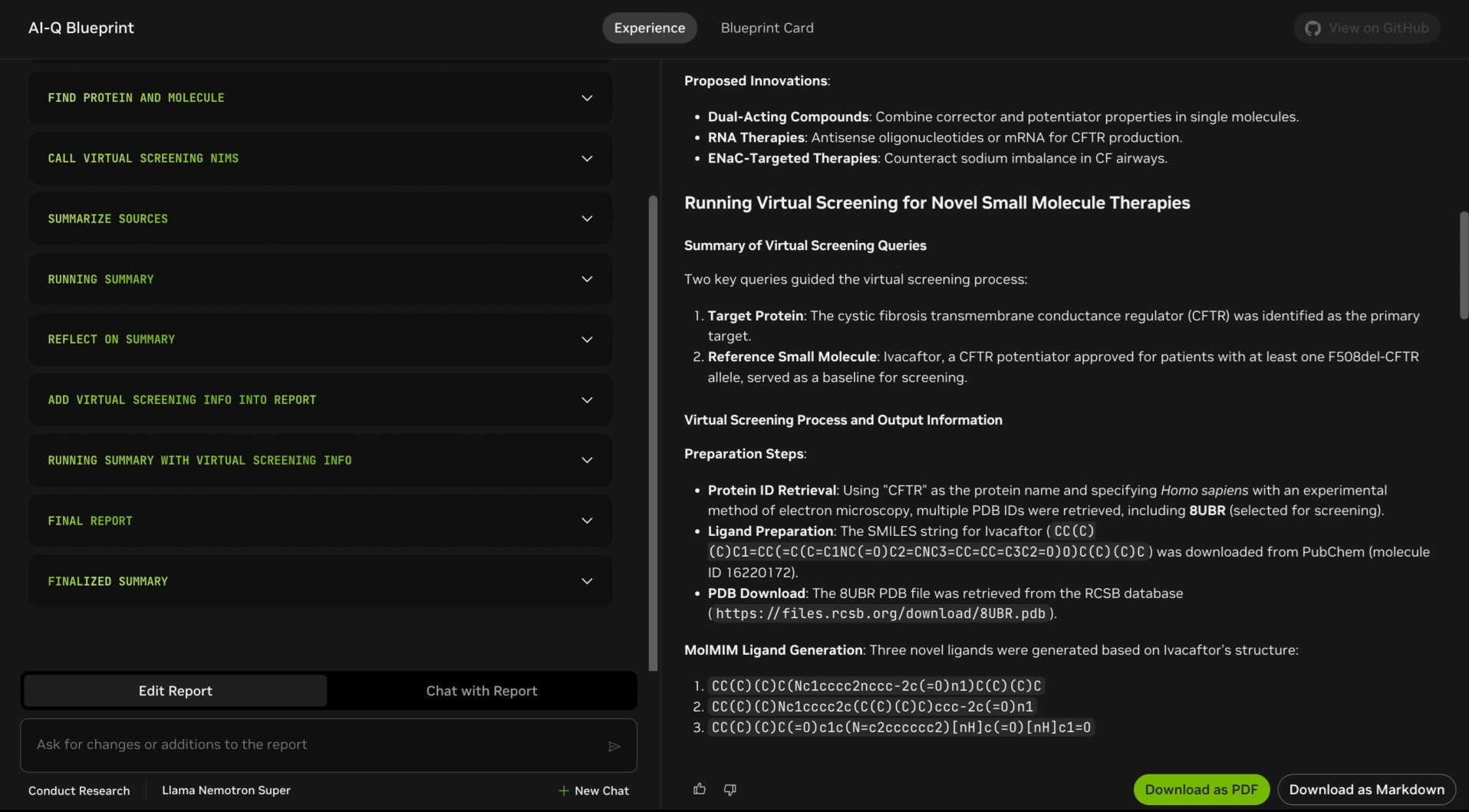
AI-Q Blueprint UI
The blueprint is available in two modes:
-
GitHub Repository: Customizable code for self-hosted NIM microservices, allowing integration with proprietary datasets. This option allows users to deploy within their own hardware infrastructure and build local knowledge bases for secure, tailored use cases.
-
NVIDIA Brev Launchable: A cloud-hosted UI with example datasets and an interactive environment enabling end-to-end virtual screening without specialized hardware.
One of the stated advantages is traceability: the system reportedly logs reasoning steps, which could support intellectual property claims in research workflows where explainability and reproducibility are critical. According to the team, this aligns with regulatory expectations in domains where only 1 in 5,000 candidate compounds ultimately receive FDA approval.
Another challenge addressed by the system is hypothesis development. Traditional search tools return static information, whereas NVIDIA’s agentic framework is designed to simulate multi-criteria reasoning where it is evaluating chemical binding, synthetic feasibility, and therapeutic potential in tandem. This integration is designed to help with faster and more context-aware target validation.
The blueprint is part of a broader set of agentic tools from NVIDIA targeting life sciences R&D, and was developed by a team including Vega Shah, Katie Link, Jin Li, Raghav Mani, and others. Documentation and open-source components are available on GitHub and the NVIDIA technical blog.
Topic: Tech Giants