Xaira Publishes Largest Public Perturb-seq Atlas to Advance Virtual Cell Modeling
Xaira Therapeutics has announced the release of "X-Atlas/Orion", a large genome-wide Perturb-seq dataset, reportedly the largest publicly available resource of its kind. The dataset includes information from 8 million individual cells, targeting all human protein-coding genes, with deep sequencing coverage of over 16,000 unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) per cell.
This resource was generated using Xaira's "Fix-Cryopreserve-ScRNAseq" (FiCS) Perturb-seq platform, which leverages the Chromium system from 10x Genomics. According to Xaira, the platform addresses common limitations associated with large-scale single-cell data collection, including sensitivity, scalability, and reproducibility. Xaira’s team indicates that FiCS Perturb-seq reliably captures transcriptional changes resulting from gene perturbations and effectively reflects known biological pathways.
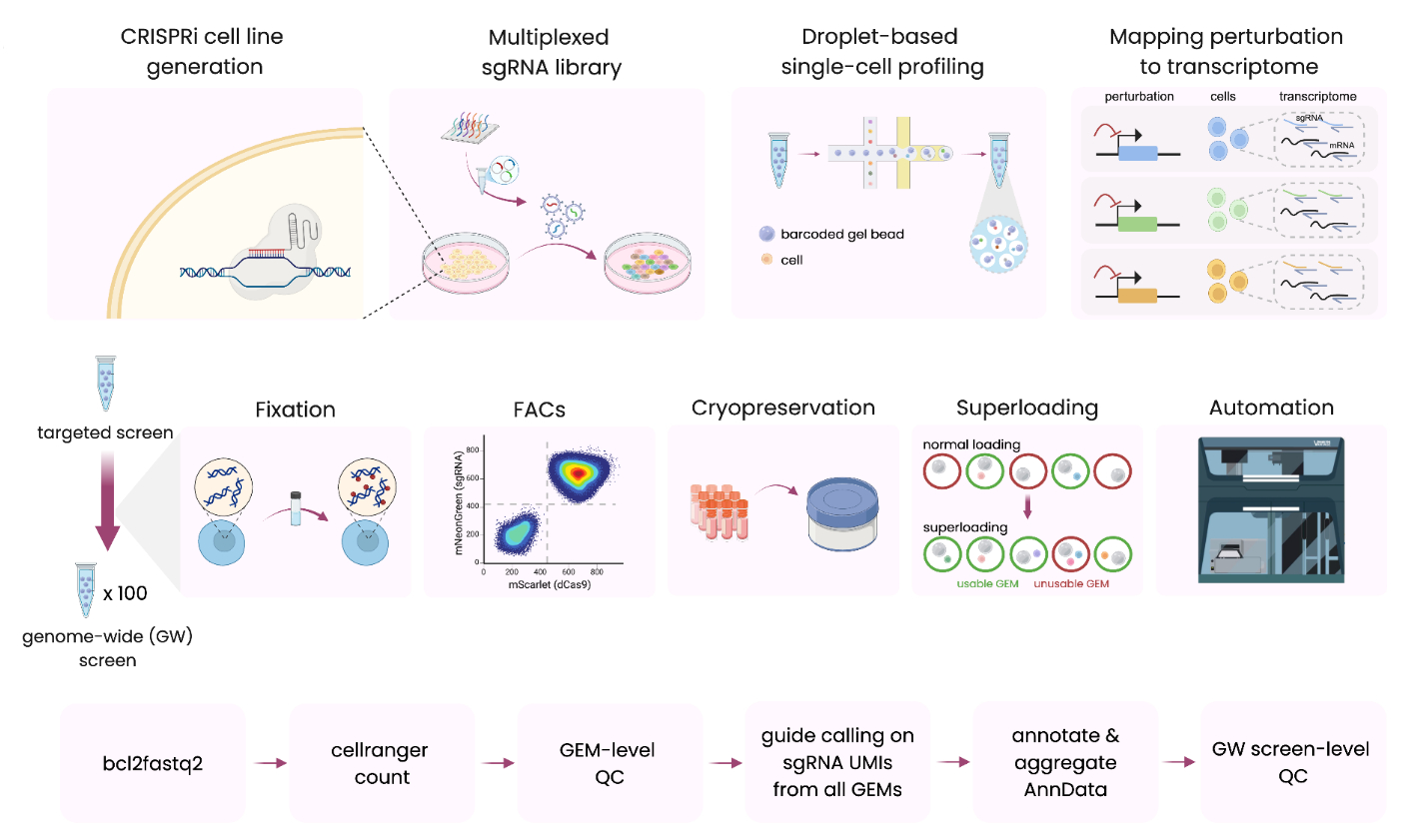
Overview of Xaira’s FiCS Perturb-seq platform and associated computational pipeline, including generation of stable CRISPRi cell lines, pooled sgRNA delivery, high-throughput single-cell library preparation and sequencing, followed by end-to-end computational analysis—from sequencing reads to annotated, analysis-ready AnnData objects. Detailed caption in source; adapted from Xaira Therapeutics' preprint (BioRender).
In parallel with the dataset release, Xaira published details of its computational approach to identify dose-dependent genetic effects. Traditionally, Perturb-seq gene knockdowns have been analyzed as binary outcomes, with genes viewed as either active or suppressed. Xaira’s researchers instead measure the abundance of single guide RNA (sgRNA) detected in each cell to quantify the level of gene suppression, introducing a continuous, rather than binary, scale. According to Xaira, this refined framework potentially improves the precision and predictive capability of models that attempt to interpret gene functions.
Xaira, launched in April 2024 with $1 billion in funding, aims to integrate artificial intelligence with biological data to accelerate drug discovery and development. The company is headed by former Stanford president Marc Tessier-Lavigne, and its co-founder, David Baker (co-laureate of the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for protein structure prediction). Bo Wang, recently appointed SVP and head of biomedical AI, stated the dataset could contribute to the training of virtual cell models, designed to simulate cellular responses to various perturbations.
Access the Dataset:
X-Atlas/Orion is now publicly available here: https://doi.org/10.
Read the Preprint:
FiCS Perturb-seq and X-Atlas/Orion publication: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.06.11.659105v1
Topic: AI in Bio