Somite AI Retitles as Cellular Intelligence in Pursuit of a Universal Virtual Cell Signaling Model
Founded in 2023 and based in Boston, Cellular Intelligence becomes the new identity of Somite AI, expanding toward large-scale, dynamic modeling of cell signaling. Alongside the rebrand, the company has released a technical white paper that describes its data-generation system, experimental scale-up and early validation steps for a new virtual cell signaling model intended to capture sequential, combinatorial inputs that drive cell fate.
The company’s original focus was to build a “life language model” to guide the formation of somites—the embryonic precursors of the musculoskeletal system—and apply this to cell replacement therapies for conditions such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, a common hereditary neuromuscular disease.
With the new Cellular Intelligence branding, the company is now presenting a wider scope, using their microfluidic capsule platform to expose healthy pluripotent stem cells to carefully controlled sequences of external signals and record how the cells change at each step. The aim is to learn the rules by which combinations, strength and timing of signals steer cells into different potential states. Over 2025, the company reports expanding its capsule-based platform from a 27,000-condition pilot to more than one million ordered signal combinations.
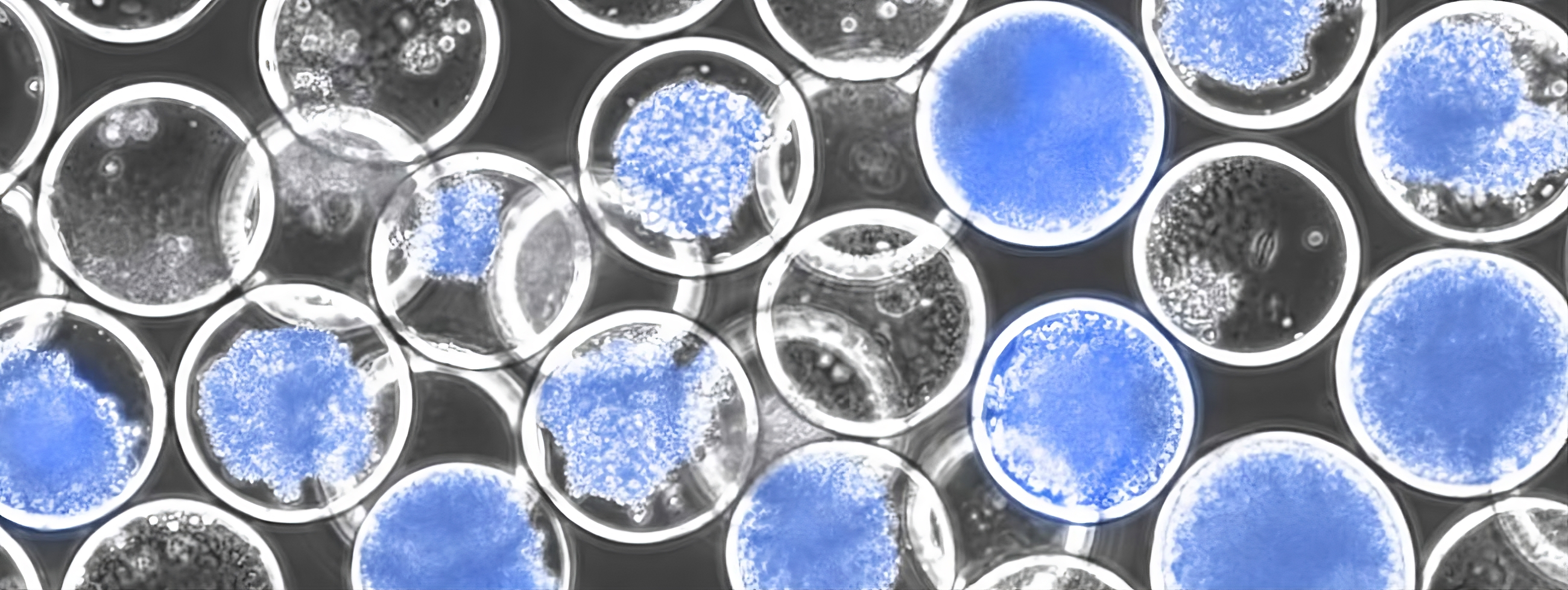
From the whitepaper: Cellular Intelligence describes semi-permeable capsules as a central element of its technology stack, used to run sequential signaling experiments at a scale it argues peers cannot currently replicate. The blue stain indicates cells differentiating along the ectoderm lineage.
The white paper outlines how the group maps healthy developmental pathways as a reference for interpreting disease-related deviations, given that most human cell states arise from permutations of approximately 20 major signaling pathways. The team reports adapting Transformer architectures commonly used in language models to predict a cell’s next state from its current state plus a sequence of external cues. Through an active-learning loop, model uncertainty is used to select the next batch of experiments, prioritizing signal combinations where predictions are weak or missing.
For example, the platform reportedly recovered a protocol for generating a rare developmental cell type that had only recently been described in the literature, which the team presents as evidence that the platform can surface useful, previously unknown signal combinations.
The company’s leadership includes academic researchers from Harvard Medical School and the University of Pennsylvania. Cellular Intelligence also reports raising more than 62 million dollars to date from investors including Khosla Ventures, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, SciFi VC, AMD Ventures and Fusion Fund, with the latest $47 million Series A in May 2025.
The move comes amid broader efforts to build virtual cell infrastructure. To name a few, Arc Institute and Tahoe Therapeutics launched the Arc Virtual Cell Atlas, built on Tahoe-100M and scBaseCount. Ginkgo Bioworks started the open-source Virtual Cell Pharmacology Initiative to generate over 12 billion pharmacological data points, Xaira released an 8 million-cell genome-wide Perturb-seq atlas, and Latch Bio followed with a 25 million-cell spatial transcriptomics atlas spanning 45 tissues and 63 diseases.
Our deep dive, Building the Virtual Cell: AI Foundation Models and Billion-Cell Datasets, places efforts like Cellular Intelligence in an even longer arc that runs from early whole-cell simulations in the 2000s concept built on foundation models, perturbation atlases and lab-in-the-loop systems.
Topic: AI in Bio