Researchers Use Terahertz Imaging for First-Ever 3D View of Cochlea Without Surgery
In a study published March 27 in Optica, researchers from Waseda, Kobe, and Osaka Universities reported the successful use of terahertz (THz) imaging to non-invasively visualize the internal structure of the mouse cochlea. The work marks the first demonstration of THz-based 3D imaging of cochlear tissue and suggests future applications in diagnostics for hearing loss, dermatology, and potentially early-stage cancers.
The cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear essential for hearing, is difficult to image due to its location and delicate structure. Existing imaging methods often fall short in resolution or require invasive procedures. To address this, the team developed a micrometer-scale THz point source using a femtosecond laser and GaAs substrate, enabling near-field imaging of cochlear tissue placed directly on the chip. The resulting data were processed using time-of-flight depth conversion and k-means clustering to extract structural features and reconstruct the cochlea in 3D.
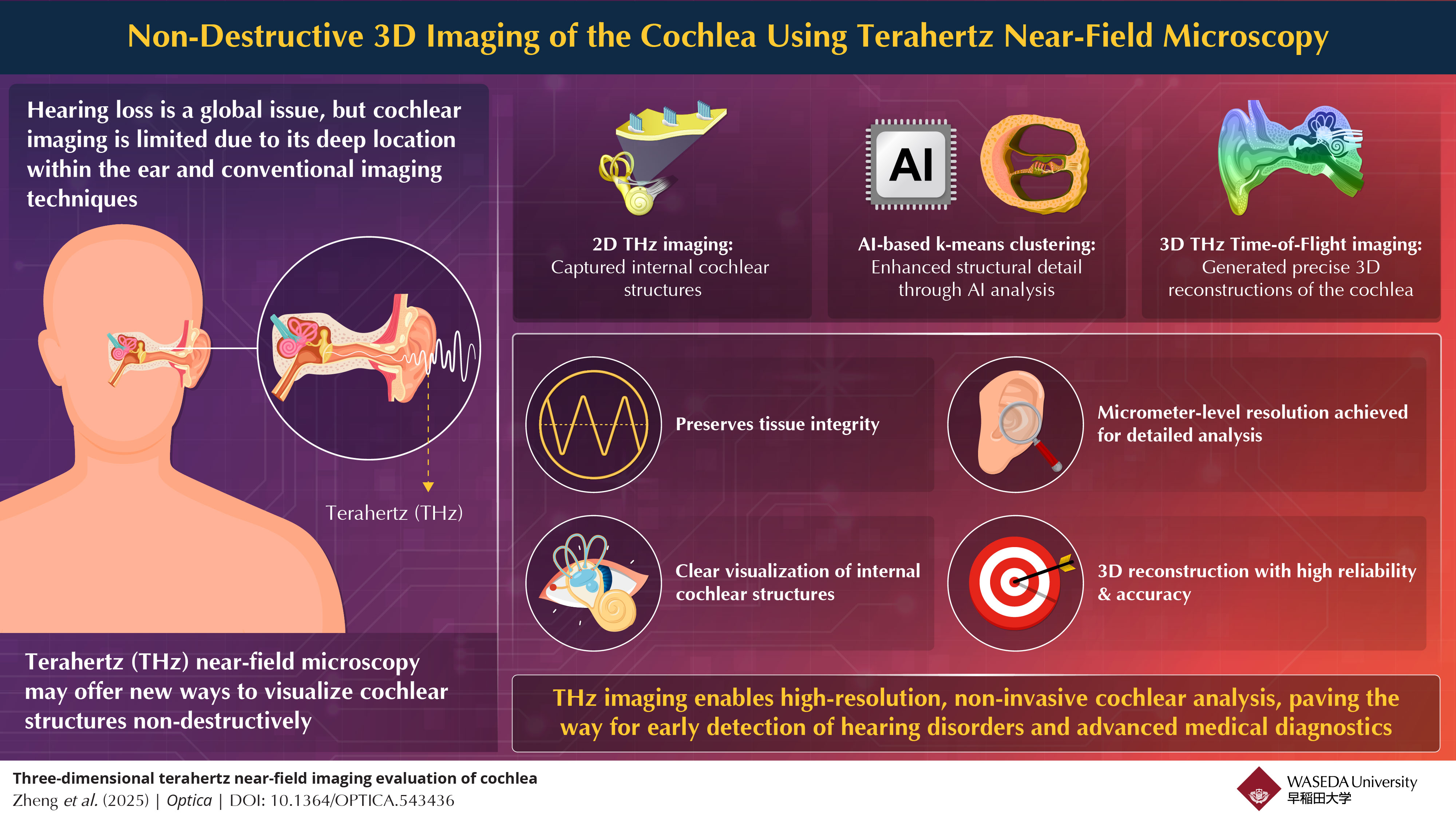
The technique produced high-resolution images at varying depths, revealing internal cochlear architecture and enabling detailed 3D reconstructions. The researchers propose that this method could be adapted into compact medical tools such as THz endoscopes or otoscopes for in vivo diagnostics. According to lead author Associate Professor Kazunori Serita, integration of THz imaging into medical devices could accelerate diagnostic timelines and improve accuracy, particularly in fields like oncology and pathology.
While still in the early stages and demonstrated only in animal models, the findings offer a proof of concept for THz imaging as a potentially scalable and non-destructive diagnostic tool. Future development will determine whether the technique can be miniaturized and applied effectively in clinical settings.