Pusan National University Researchers Develop AI Model to Identify Therapeutic Gene Targets Using Hypergraphs
A team from Pusan National University, led by Associate Professor Giltae Song, has developed a new artificial intelligence model called the Hypergraph Interaction Transformer (HIT) to improve the identification of therapeutic gene targets.
The research was published in Briefings in Bioinformatics (January 2025, Vol. 26, Issue 1).
Unlike conventional deep learning models that struggle to capture the complex many-to-many relationships between diseases, genes, and ontologies, HIT uses hypergraph structures and attention-based encoders to represent these associations more effectively. The model constructs separate gene and disease hypergraphs from biological datasets and processes them using a two-stage encoding system to classify genes as therapeutic targets, biomarkers, or unrelated.
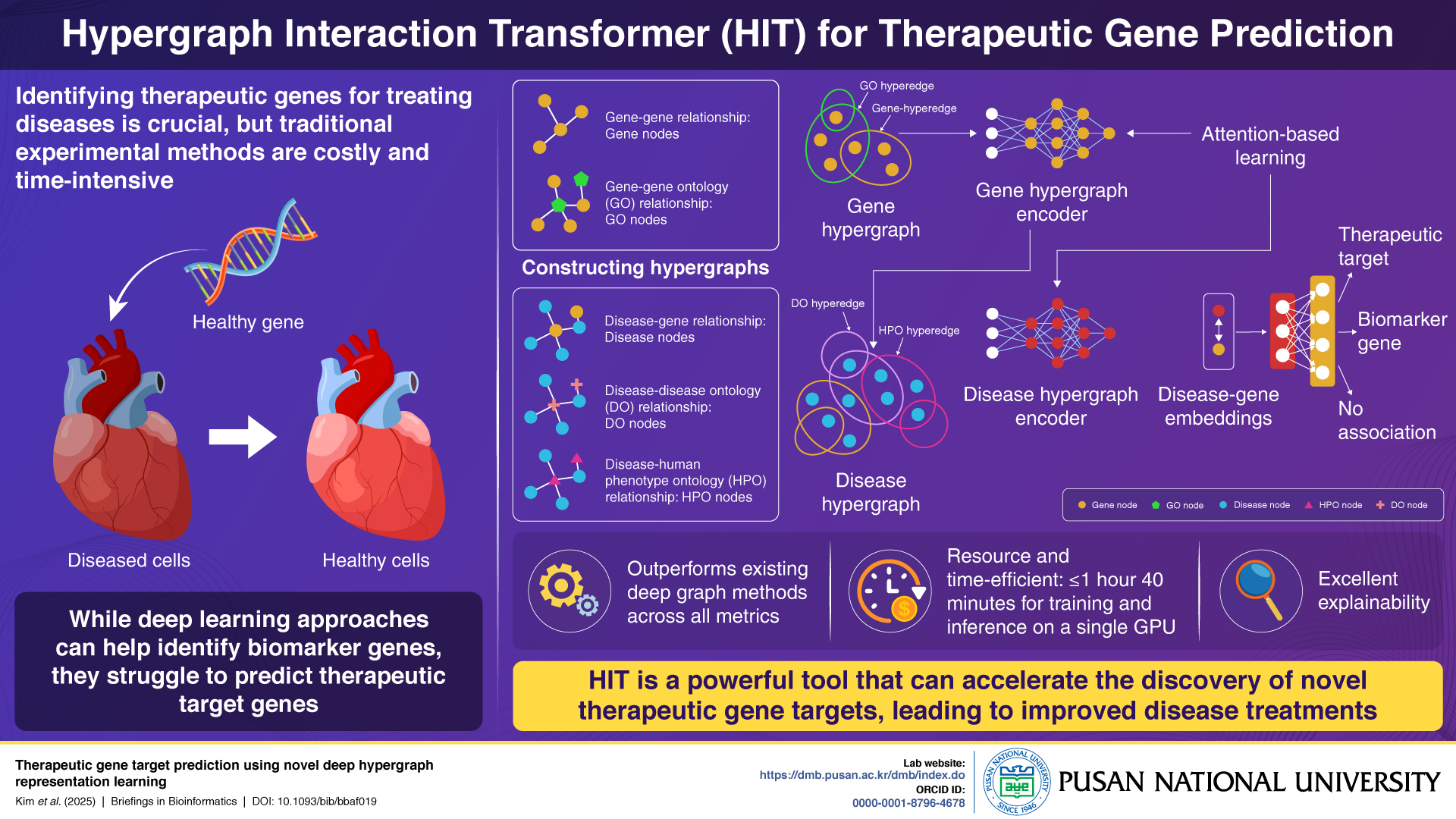
In benchmark testing, HIT outperformed all existing models across evaluation metrics and required only 1 hour and 40 minutes of GPU-based training and inference time. A case study on heart failure showed the model successfully identified all known therapeutic targets. The researchers emphasize HIT’s explainability as a key feature, enabling transparency in how gene-disease associations are determined—critical for clinical and translational research.
The model is intended to shorten the drug development pipeline and enhance the precision of early-stage therapeutic research, particularly in the context of personalized medicine.