Consensus and Biomni Integrate Agentic AI into Biomedical Literature Research
Biomni, an open-source biomedical AI agent, has recently integrated the Consensus academic search engine into its architecture. Consensus contributes a large, curated corpus and AI-based retrieval, while Biomni layers large language model reasoning, retrieval-augmented planning, and code execution to generate structured analyses. The integration is intended to support biomedical questions that typically require manual literature review.
Consensus, founded in 2021 by Christian Salem and Eric Olson, is an AI-based academic search engine built to improve access to scientific knowledge. The platform indexes more than 200 million documents drawn from Semantic Scholar, OpenAlex, and its own web crawl, covering high-impact journals and the entirety of PubMed.
Searches combine AI-driven semantic matching with traditional keyword methods to balance intent recognition with precise term matching. Results are filtered by recency, citation count, and journal reputation, then summarized using a mix of commercial and fine-tuned open-source models. Consensus operates as a retrieval-first engine: papers are always real, cited, and linked back to their original sources, with AI used only for summarization and synthesis.
Biomni’s architecture is split into two layers: a mapped environment of biomedical tools and databases (Biomni-E1), and a generalist agent framework (Biomni-A1) that dynamically composes workflows across genomics, drug discovery, rare diseases, and molecular biology. This allows researchers to issue natural language queries that trigger end-to-end literature analysis, data integration, and interpretation.
Benchmarking AI Search Against Traditional Tools
In comparative testing, conducted by Biomni, Consensus was evaluated against other search methods using the query: “Find papers published in 2023–2024 comparing prime editing versus base editing efficiency for correcting point mutations in the CFTR gene.” Consensus retrieved 22 relevant papers in 6 seconds. By comparison, Google Scholar surfaced 1 paper in 2 seconds, PubMed failed to return any relevant results after multiple attempts, and arXiv produced 20 largely unrelated papers with minimal biological relevance. Claude’s advanced web search returned 16 papers in 35 seconds. Consensus results were delivered in structured form with abstracts, making downstream interpretation faster.
Case Study: Variant Mechanism Interpretation
In one test, Biomni was asked to explore the single nucleotide polymorphism rs2227982 in the PDCD1 gene. The task involved mapping its molecular function, reviewing disease associations, and assessing its potential as a biomarker for immunotherapy response.
To generate the analysis, the agent combined queries across genomic databases, literature on protein function, population frequency datasets, and clinical trial records. It integrated findings on how the variant alters PD-1 signaling, its frequency across different populations, and its reported links to autoimmune disorders, cancer, and checkpoint inhibitor therapy outcomes.
The structured summary below illustrates the output Biomni produced:
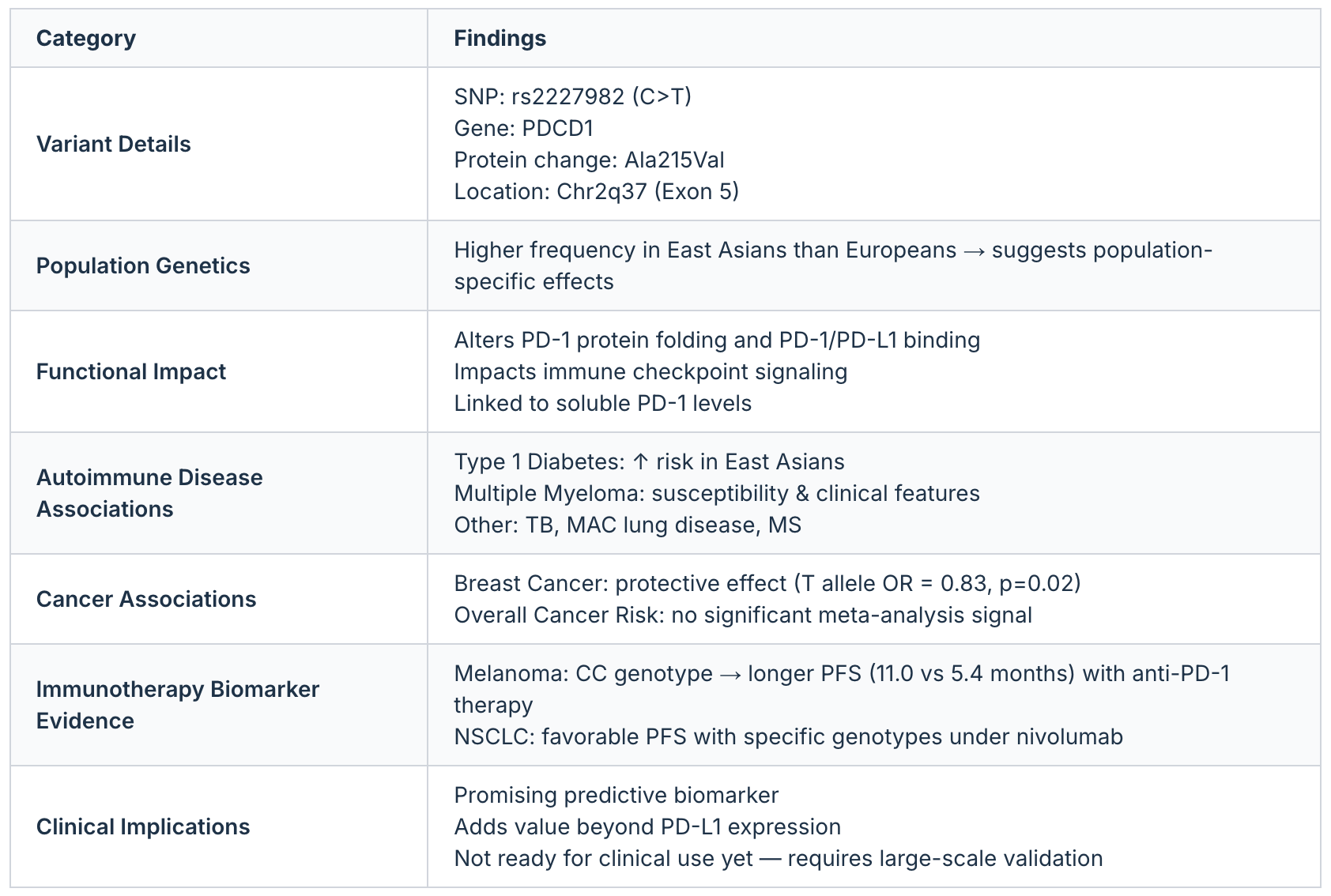
Image credit: Case Study 2: Variant Mechanism Interpretation
The results were assembled from a range of functional studies, genetic association papers, and clinical trial reports, all of which are listed in the supporting literature here.
Biomni remains open source, with resources including the web interface, source code on GitHub, and a published paper describing the underlying framework. Consensus is accessible through a tiered subscription model with a free to use version. The integration is designed to reduce the time spent on manual literature review, shifting the focus back to experimental design and hypothesis generation.
Topic: AI in Bio